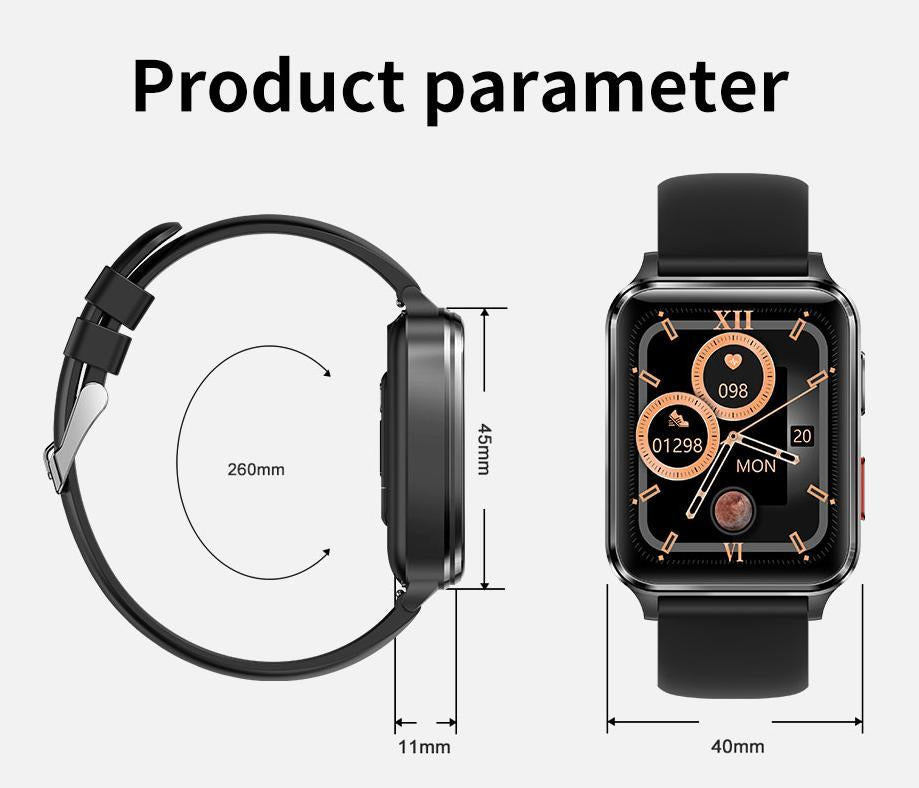
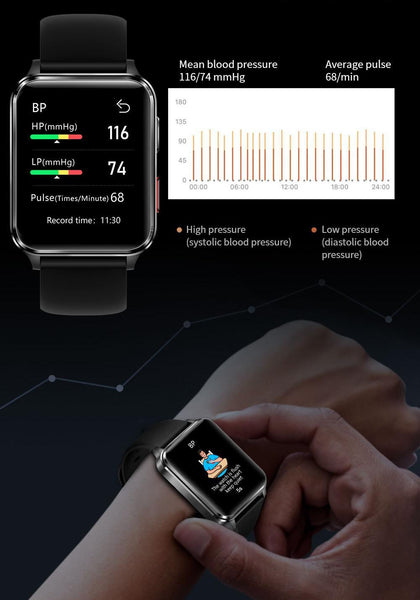
Unlock The Power of BP Doctor Smartwatch Heart Rate
See how our first automatic, continuous wrist based heart rate technology is helping you understand your heart on a new level.
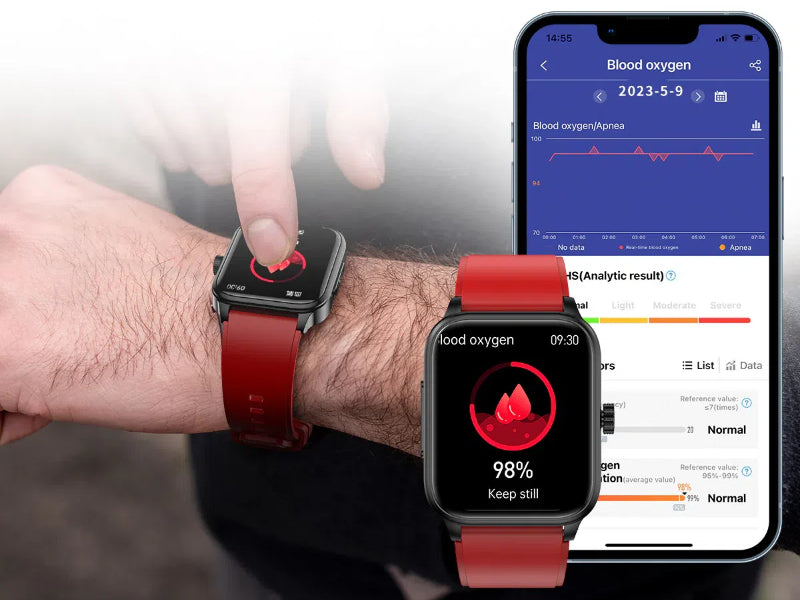
Understanding Blood Oxygen Monitoring on Smartwatches
Comment choisir le bon tracker de fitness

Comment les montres intelligentes révolutionnent le fitness et le bien-être

Conseils sur le sommeil : 6 étapes pour mieux dormir
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring: a type of blood pressure monitoring in which the person wears a cuff attached to a portable device that is worn on the person’s waist and takes a blood pressure reading at regular intervals during the day for 24 hours. This is to calculate their average blood pressure. A GP may suggest this if they think a person has high blood pressure.
Ambulatory ECG monitoring: a form of monitoring the heart’s electrical activity for 24 to 48 hours, in which three electrodes attached to the chest are connected to a device worn on the waist.
Abdominal aortic aneurysm: a bulge or swelling in the aorta, the main blood vessel that runs down the chest and tummy from the heart. High blood pressure can cause this serious health condition.
Accupro/accupril: a brand name of the ACE inhibitor quinapril.
Accuretic: a brand name of the ACE inhibitor quinapril combined with the diuretic hydrochlorothiazide.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor: a medicine used to treat heart failure and high blood pressure. They’re often prescribed to people who have had a heart attack. ACE inhibitors reduce the activity of an enzyme called angiotensin-converting enzyme that has a narrowing effect on the blood vessels and increases blood pressure.
Acepril: a brand name of the ACE inhibitor captopril.
Acezide: a brand name of the ACE inhibitor captopril combined with the diuretic hydrochlorothiazide.
Acromegaly: a condition in which the body produces too much growth hormone (GH), causing bones and bodily tissues to grow more quickly. Also a potential cause of high blood pressure.
Adalat: a brand name of the calcium channel blocker nifedipine.
Adipine: a brand name of the calcium channel blocker nifedipine.
Adizem: a brand name of the calcium channel blocker diltiazem.
Aldactone: a brand name of the diuretic spironolactone.
Alpha blockers: a type of blood pressure medication that lowers blood pressure by relaxing the blood vessels so blood can flow through them more easily
American Heart Association (AHA): a non-profit organisation in the US that funds cardiovascular medical research, educates the public on healthy living and fosters care to help to reduce deaths and disability caused by strokes and cardiovascular disease.
Amias: a brand name of the ARB candesartan.
Amlodipine: a type of calcium channel blocker.
Angina: persistent chest pain, a possible symptom of high blood pressure. Learn more about angina here.
Angiotensin II: a hormone that has a powerful constricting effect on the blood vessels and causes salt and water retention in the body, which raises blood pressure.
Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB): drugs used to treat heart failure and high blood pressure. ARBs operate by reducing the actions of angiotensin II. They block the AT1 receptors, the receptors the hormone acts upon.
Aprinox: a brand name of the diuretic bendroflumethiazide.
Aprovel: a brand name of the ARB irbesartan.
Arrhythmia: a problem with the rate or rhythm of the heartbeat. The heart can beat too fast, too slow or the rhythm can be irregular during arrhythmia.
Arteries: vessels in the body that carry blood away from the heart.
Atenolol: a type of beta blocker medicine.
Atheroma: a fatty material also called ‘plaques’ that can clog up arteries and cause blood pressure to increase. Atherosclerosis: narrowing of the arteries.
Atorvastatin: a high-intensity statin i.e. a statin that can reduce low-density lipoprotein (also known as ‘bad’ cholesterol) by more than 40%.
Atrial fibrillation: a heart condition that causes an irregular, often abnormally fast heartbeat. The condition can affect people who live with high blood pressure. Learn more about atrial fibrillation here.
Atrial flutter: a similar condition to atrial fibrillation, but the rhythm in the atria is more organised and less chaotic than the abnormal patterns atrial fibrillation causes.
Atrium: one of two upper chambers of the heart. The plural of atrium is ‘atria’.
Autonomic nervous system: a component of the peripheral nervous system that regulates involuntary physiological processes, including blood pressure.
Automatic, upper-arm monitor: a monitor that measures blood pressure at the upper arm.
Bendroflumethiazide: a type of diuretic used to treat high blood pressure.
Beta blocker: a common and important drug that lowers blood pressure, mainly by slowing down the heart; by stopping the actions of hormones such as adrenaline.
Betaloc: a brand name of metoprolol, a beta blocker medicine.
Bisoprolol: a type of beta blocker medicine.
Bladder: the inflatable bag of the blood pressure monitor cuff.
Blood pressure: the force exerted by the blood against the walls of the body’s arteries, the major vessels in the body.
Body mass index (BMI): a measure of height and weight to calculate if you are a healthy weight.
British and Irish Hypertension Society (BIHS): a forum for professionals who work in the fields of hypertension and cardiovascular disease in the UK and Ireland.
British Medical Association (BMA): the trade union and professional body for doctors and medical students in the UK.
British Medical Journal (BMJ): a weekly medical trade publication, published by the British Medical Association.
Calcium channel blockers (CBBs): a group of medicines used to treat heart conditions and blood vessel conditions, including hypertension, angina and abnormal heart rhythm. Calcium channel blockers operate by stopping calcium from entering the cells of the heart and arteries.
Candasartan: a type of ARB (Angiotensin receptor blockers).
Capoten: a brand name of the ACE (Angiotensin-converting enzyme) inhibitor captopril.
Capozide: a brand name of the ACE (Angiotensin-converting enzyme) inhibitor captopril.
Capozide LS: a brand name of the ACE (Angiotensin-converting enzyme) inhibitor captopril.
Captopril: an ACE inhibitor.
Carace: a brand name of the ACE inhibitor lisinopril.
Carace Plus: a brand name of the ACE inhibitor lisinopril.
Cardiac index (CI): the volume of blood in litres per minute pumped by the heart around the body divided by the body surface area (l/min/m2).
Cardicor: a brand name of bisoprolol, a beta blocker medicine
Cardioplen: a brand name of the calcium channel blocker felodipine.
Cardiovascular disease: another term for heart disease and stroke.
Cardioversion: a treatment for atrial fibrillation in which the heart is given a controlled electric shock to restore normal rhythm.
Cardura: a brand name of the alpha blocker doxazosin.
Carvedilol: a type of beta blocker medicine.
Cardiac event recorder: A small recording device for people who suffer infrequent palpitations or collapses. The user holds it to their chest when symptoms start and records their heart rhythm.
Catheter ablation: a treatment for atrial fibrillation that uses radio frequency energy to destroy the area inside the heart causing the abnormal heart rhythm.
Centrally acting agents: a type of drug used to treat high blood pressure. The drug acts on alpha₂-adrenoreceptors in the brain stem and reduces peripheral vascular resistance and, as result, blood pressure.
Cilazapril: an ACE inhibitor.
Clinical trial: a research study that compares the effects of one treatment with another.
Coarctation: a condition that involves tightening of the aorta, the main artery on the left side of the heart, and restricts normal blood flow.
Congescor: a brand name of the beta blocker bisoprolol.
Coracten: a brand name of the calcium channel blocker nifedipine.
Coversyl: a brand name of the ACE inhibitor perindopril.
Coversyl Plus: a brand name of the ACE inhibitor perindopril.
Cozaar: a brand name of the ARB losartan.
Cuff: an inflatable band wrapped around the arm when monitoring blood pressure.
Cushing’s syndrome: a condition caused by having too much cortisol hormone in the body. Also a potential cause of high blood pressure.
Diabetes: a condition in which glucose (sugar) levels in the blood are too high. High blood pressure can place a person at risk of diabetes.
Diastolic blood pressure: the resistance to the blood flow in the vessels. This is the lower number on a blood pressure reading.
Diltiazem: a type of calcium channel blocker.
Diovan: a brand name of the ARB valsartan.
Direct renin inhibitors: a relatively new class of drug used to treat high blood pressure. Aliskiren is the only licensed one so far and operates by competing with angiotensinogen for access to the active site of the renin enzyme. The drug reduces plasma renin activity and causes a sustained reduction in angiotensin I and II levels.
Diuretic: a drug given to people who have high blood pressure or who are retaining fluid. Diuretics work by encouraging you to pass water more to get rid of excess salts and fluids, which lowers the volume in the blood and, as a result, lowers blood pressure.
Doppler test: a blood flow detection test that shows whether there is a pulse and whether there is blood flow to a limb.
Dosette box: a pill box that has different compartments for each day and, if necessary, each time of the day.
Doxadura: a brand name of the alpha blocker doxazosin.
Doxazosin: a type of alpha blocker used to treat high blood pressure.
Electrocardiogram: a test that records the rhythm, rate and electrical activity of a person’s heart.
Emcor: a brand name of bisoprolol, a beta blocker medicine.
Enalapril: an ACE inhibitor. A brand of this ACE inhibitor also goes by this name.
Esmolol: a type of beta blocker medicine.
European Society of Hypertension (ESH): a platform for scientific exchange in hypertension.
Familial hypercholesterolaemia: a genetic condition in which the individual has high levels of cholesterol in their blood. The condition is passed down through families and is caused by one or more faulty genes.
Felodipine: a type of calcium channel blocker.
Felotens: a brand name of the calcium channel blocker felodipine.
Folpik: a brand name of the calcium channel blocker felodipine.
Fortipine: a brand name of the calcium channel blocker nifedipine.
Fosinopril: an ACE inhibitor. A brand of the inhibitor also takes this name.
Glomerulonephritis: damage to the tiny filters inside the kidneys, and a potential cause of high blood pressure.
Gopten: a brand name of the ACE inhibitor trandolapril.
Hawthorne effect: a type of reactivity in which individuals alter an aspect of their behaviour in response to their awareness of being observed.
Heart palpitations: moments when the heartbeat becomes more noticeable. It may feel as if it’s fluttering, pounding, beating irregularly, racing or beating very fast.
High blood pressure (hypertension): when blood pressure is too high.
Holter monitoring: another term for 24 hour ECG recording.
Home blood pressure testing: the practice of conducting blood pressure tests at home using your own blood pressure monitoring device.
Hypertension: the medical term for ‘high blood pressure’, a condition in which the pressure in blood vessels is unusually high.
Hypotension: a term for when blood pressure is lower than expected. Also known simply as ‘low blood pressure’.
IEEE: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers.
Imidapril: an ACE inhibitor.
Implantable loop recorder (ILR): a small heart monitor fitted under the skin to monitor the rhythm of the person’s heart for up to three years.
Indapamide: a type of diuretic used to treat high blood pressure.
Inderal: a brand name of metoprolol, a beta blocker medicine.
Innovace: a brand name of the ACE inhibitor enalapril.
Innozide: a brand name of the ACE inhibitor enalapril.
Intermittent claudication: a medical term that describes the painful ache you suffer in your legs when you walk if you have peripheral arterial disease, but which disappears after a few minutes of rest
International Society of Hypertension (ISH): a not-for-profit organisation devoted to innovation and advances in the field of hypertension.
Irbesartan: a type of ARB.
Istin: a brand name of the calcium channel blocker amlodipine.
Larbex: a brand name of the alpha blocker doxazosin.
Lisinopril: an ACE inhibitor. A brand of the drug also goes by this name.
Lopressor: a brand name of propranolol, a beta blocker medicine
Low blood pressure (hypotension): when blood pressure is lower than expected
Lopace: a brand name of the ACE inhibitor ramipril
Lupus: a condition in which the immune system attacks parts of the body, such as the joints, organs and skin. Also a potential cause of high blood pressure.
Masked hypertension: the phenomenon of experiencing normal blood pressure readings in a doctor or carer’s office but higher ones elsewhere.
Metabolic syndrome: a combination of high blood pressure, diabetes and being overweight that can place a person at higher risk of heart disease, stroke and other problems that involve the blood vessels.
Metoprolol: a type of beta blocker medicine.
mmHG: millimetres of mercury.
Moexipril: a type of ACE inhibitor.

Unlock The Power of BP Doctor Smartwatch Heart Rate
See how our first automatic, continuous wrist based heart rate technology is helping you understand your heart on a new level.
Nebilet: a brand name of nebivolol, a beta blocker medicine.
Nebivolol: a type of beta blocker medicine.
Neofel: a brand name of the calcium channel blocker felodipine.
Neo-Naclex: a brand name of the diuretic bendroflumethiazide.
Nifedipine: a type of calcium channel blocker.
Nifedipress: a brand name of the calcium channel blocker nifedipine.
Olmasartan: a type of ARB.
Obstructive sleep apnoea: a type of sleep apnoea in which the walls of the throat narrow and relax while the person is sleeping, interrupting normal breathing.
Olmetec: a brand name of the ARB olmesartan.
Pacemaker: a small, electrical device that is surgically implanted in a person’s chest and sends electrical pulses to their heart to keep it beating regularly and not too slowly.
Parmid: a brand name of the calcium channel blocker felodipine.
Perdix: a brand name of the ACE inhibitor moexipril.
Perindopril: a type of ACE inhibitor.
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD): a common condition in which a build-up of fatty deposits in the arteries restricts blood supply to the legs.
Peripheral vascular disease (PVD): another name for peripheral arterial disease.
Pheochromocytoma: a rare tumour of the adrenal glands, which sit above the kidneys, and is a potential cause of high blood pressure.
Plendipine: a brand name of the calcium channel blocker felodipine.
Potent direct vasodilators: a type of drug used to treat high blood pressure.
Pravastatin: a low-intensity statin i.e. a statin that can reduce low-density lipoprotein (also known as ‘bad’ cholesterol) by around 20 to 30%.
Propranolol: a type of beta blocker medicine.
Pulmonary hypertension: a condition in which the blood pressure in the blood vessels leading from the heart to the lungs is too high.
Quinapril: a type of ACE inhibitor.
Ramipril: a type of ACE inhibitor.
Raporsin: a brand name of the alpha blocker doxazosin.
Recalibration: testing and adjusting a blood pressure monitoring device to ensure it’s still accurate.
Renal artery: artery that supplies blood to the kidney.
Renal stenosis: a narrowing of one or more of the arteries that carry blood to the kidneys.
Renin: an enzyme the kidneys release that plays a role in blood pressure regulation.
Rosuvastatin: a high intensity statin i.e. a statin that can reduce low-density lipoprotein (also known as ‘bad’ cholesterol) by more than 40%.
Scleroderma: a condition that causes thickened skin and sometimes creates problems with organs and blood vessels. Scleroderma is a potential cause of high blood pressure.
Secondary hypertension: high blood pressure caused by an identifiable secondary condition, such as kidney disease or diabetes.
Securon: a brand name of the calcium channel blocker verapamil.
Self-measured blood pressure (SMBP) monitoring: the practice of measuring your blood pressure at home regularly.
Simvastatin: a low-intensity statin i.e. a statin that can reduce low-density lipoprotein (also known as ‘bad’ cholesterol) by around 20 to 30%.
Sleep apnoea: a condition in which breathing starts and stops while the person is sleeping.
Slocin: a brand name of the alpha blocker doxazosin.
Slozem: a brand name of the calcium channel blocker diltiazem.
Spironolactone: a type of diuretic used to treat high blood pressure. Can be used when other medicines haven’t worked.
Staril: a brand name of the ACE inhibitor fosopril
Statins: drugs that lower the body’s cholesterol. The main difference between statins is the amount they lower cholesterol. Statins can be low-intensity statins or high-intensity ones.
Sphygmomanometer: technical name for a blood pressure monitor.
Stroke: a serious, life-threatening condition that occurs when part of the blood supply to the brain is cut off.
Suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN): a bilateral structure in the anterior part of the hypothalamus in the brain. The structure is the central pacemaker of the circadian timing system and regulates the majority of the body’s circadian rhythms.
Systolic blood pressure: (the higher number) the force the heart pumps blood around the body.
Tanatril: a brand name of the ACE inhibitor imidapril.
Tarka: a brand name of the ACE inhibitor trandolapril.
Tenormin: a brand name of atenolol, a beta blocker medicine.
The Lancet: a medical journal.
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE): an executive, non-departmental public body, sponsored by the Department of Health, that provides guidance and advice to improve health and social care.
Thiazide: a type of diuretic used to treat blood pressure by reducing sodium and urine volume in the blood and lowering peripheral resistances by altering responses in the contraction of smooth muscle.
Tildiem: a brand name of the calcium channel blocker diltiazem.
Trandolapril: a type of ACE inhibitor.
Triapin: a brand name of the ACE inhibitor ramipril.
Triapin Mite: a brand name of the ACE inhibitor ramipril.
Tritace: a brand name of the ACE inhibitor ramipril.
T-test: a statistical test to find out if there is a real difference in the means between two groups. Sometimes used to see if there is a significant difference in the response to treatment between groups in a clinical trial.
24 hour blood pressure monitoring: another way of saying ambulatory blood pressure monitoring.
24 hour ECG monitoring: another term for ambulatory ECG monitoring or Holter monitoring
Valsartan: a type of ARB.
Vascalpha: a brand of the calcium channel blocker felodipine.
Vascase: a brand name of the ACE inhibitor cilazapril.
Vascular dementia: a common type of dementia caused by a reduced flow of blood to the brain. High blood pressure can cause vascular dementia.
Vascular problems: conditions that affect the blood vessels.
Venlafaxine: a type of antidepressant.
Verapress: a brand name of the calcium channel blocker verapamil.
Vera-Til: a brand name of the calcium channel blocker verapamil.
Vertab: a brand name of the calcium channel blocker verapamil.
Water pill: another name for a diuretic.
White coat effect: the phenomenon of blood pressure being higher in a doctor’s clinic because of stress, making it higher than it would be if measured at home.
White coat hypertension: the phenomenon of having elevated blood pressure readings of more than 140/90 mmHg in a doctor or carer’s office, but experiencing lower or normal readings at home. It is slightly different to white coat syndrome or white coat effect, which describes your pressure readings being higher in the clinic regardless of what the person’s numbers are.
White coat syndrome: another term for white coat effect.
Zestoretic: a brand name of the ACE inhibitor lisinopril combined with the diuretic hydrochlorothiazide.
Zestril: a brand name of the ACE inhibitor lisinopril
Sources:
Hypertension, August 2021 – https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension
How to choose a blood pressure monitor and measure your blood pressure at home – https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/heart-matters-magazine/medical/tests/blood-pressure-measuring-at-home#Heading1
High blood pressure (hypertension), October 2019 – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/high-blood-pressure-hypertension/
Home blood pressure monitoring – https://www.england.nhs.uk/ourwork/clinical-policy/cvd/home-blood-pressure-monitoring/
Secondary Hypertension, May 2019 – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21128-secondary-hypertension
What are ACE inhibitors and what do they do in your body? – https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/heart-matters-magazine/medical/drug-cabinet/ace-inhibitors
High blood pressure – symptoms and treatment – https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/risk-factors/high-blood-pressure/symptoms-and-treatment
Drug cabinet: Calcium channel blockers – https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/heart-matters-magazine/medical/drug-cabinet/calcium-channel-blockers
Drug cabinet: Diuretics – https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/heart-matters-magazine/medical/drug-cabinet/diuretics
What are beta blockers and what do they do in your body? – https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/heart-matters-magazine/medical/drug-cabinet/beta-blockers
High Blood Pressure Symptoms and Causes, May 2021 – https://www.cdc.gov/bloodpressure/about.htm
Heart Disease and Stroke, September 2022 – https://www.cdc.gov/chronicdisease/resources/publications/factsheets/heart-disease-stroke.htm
Pulmonary hypertension, December 2019 – https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/pulmonary_hypertension.htm
Pulmonary hypertension, January 2020 – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/pulmonary-hypertension/
High blood pressure (hypertension), October 2019 – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/high-blood-pressure-hypertension/causes/
Cushing’s syndrome – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/cushings-syndrome/
Acromegaly, October 2020 – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/acromegaly/
Phaeochromocytoma – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/phaeochromocytoma/
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/peripheral-arterial-disease-pad/
Vascular dementia, March 2020 – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/vascular-dementia/
Stroke, September 2022 – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/stroke/
24 hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring – https://www.gosh.nhs.uk/conditions-and-treatments/procedures-and-treatments/24-hour-ambulatory-blood-pressure-monitoring/
Blood pressure test, November 2021 – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/blood-pressure-test/
Indapamide – https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/indapamide/
Doxazosin, March 2022 – https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/doxazosin/about-doxazosin/
Spironolactone, https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/spironolactone/
Beta blockers, December 2022 – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/beta-blockers/
ACE inhibitors – https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/heart-matters-magazine/medical/drug-cabinet/ace-inhibitors
Cardiovascular disease: risk assessment and reduction, including lipid modification, September 2016 – https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg181/chapter/appendix-a-grouping-of-statins
Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) – https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/heart-matters-magazine/medical/drug-cabinet/arbs
Diuretics – https://www.bupa.co.uk/health-information/urinary-bladder-problems/diuretics
Do I need to do 24 hour blood pressure monitoring? – https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/heart-matters-magazine/medical/ask-the-experts/blood-pressure-measurement
Ask the expert: blood pressure monitoring – https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/heart-matters-magazine/medical/ask-the-experts/blood-pressure-measurement/blood-pressure-monitoring
Felodipine – https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/felodipine/
Diltiazem – https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/diltiazem/
Verapamil – https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/verapamil/
Bisoprolol – https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/bisoprolol/
Therapeutics – https://bihsoc.org/resources/therapeutics/
Atrial fibrillation, May 2021 – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/atrial-fibrillation/
Pacemaker implantation, July 2022 – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/pacemaker-implantation/
Clinical trials, December 2022 – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/clinical-trials/
European Society of Hypertension History – https://www.eshonline.org/about-esh/esh-in-brief/
What is a Doppler test? – https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/heart-matters-magazine/medical/tests/doppler-test
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence – https://www.gov.uk/government/organisations/national-institute-for-clinical-excellence
ECG – https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/tests/ecg
Frequently asked questions on diabetes – https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/heart-matters-magazine/medical/diabetes/top-questions-about-diabetes
Anatomy, autonomic nervous system, July 2022 – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539845/
Implantable loop recorders – https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/tests/implantable-loop-recorders
Heart palpitations, June 2022 – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/heart-palpitations/
Getting a blood pressure check – https://www.bloodpressureuk.org/your-blood-pressure/getting-diagnosed/getting-a-blood-pressure-check/#d.en.804811
Understanding your blood pressure – https://www.bloodpressureuk.org/your-blood-pressure/understanding-your-blood-pressure/other-related-health-problems/
What is body mass index? November 2022 – https://www.nhs.uk/common-health-questions/lifestyle/what-is-the-body-mass-index-bmi/
Angiotensin II revisited: new roles in inflammation, immunology and aging, July 2010 – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3377325/
Features and tools powered by heart rate

BP Docteur Med 14

BP DOCTEUR PRO 15

BP Docteur Pro 13

Montre intelligente ECG
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *